Get In Touch
Call: (705) 467-0701
Email: info@ortho-sport.ca
Business Hours
- Mon, Wed
- -
- Tue, Thu
- -
- Friday
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
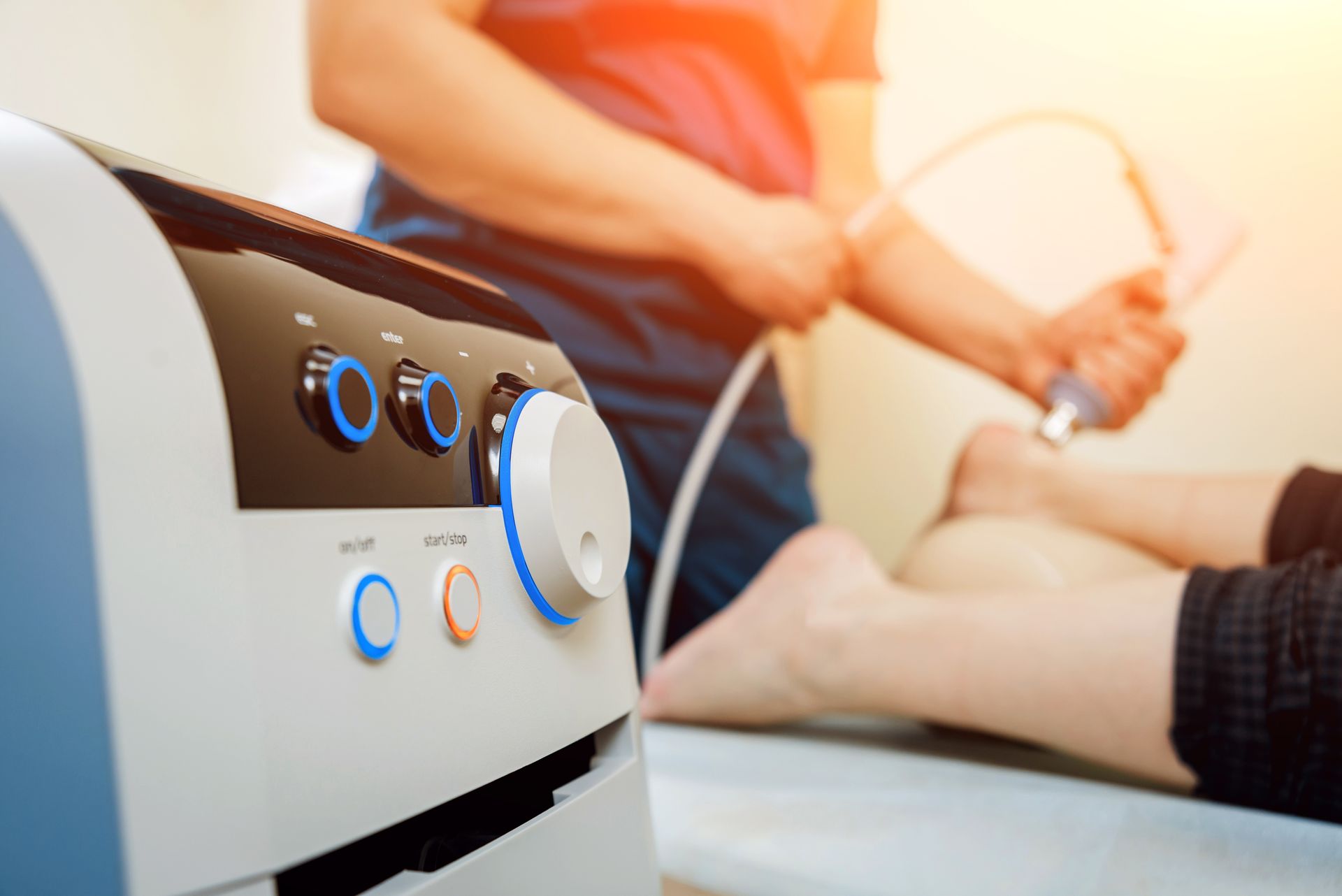
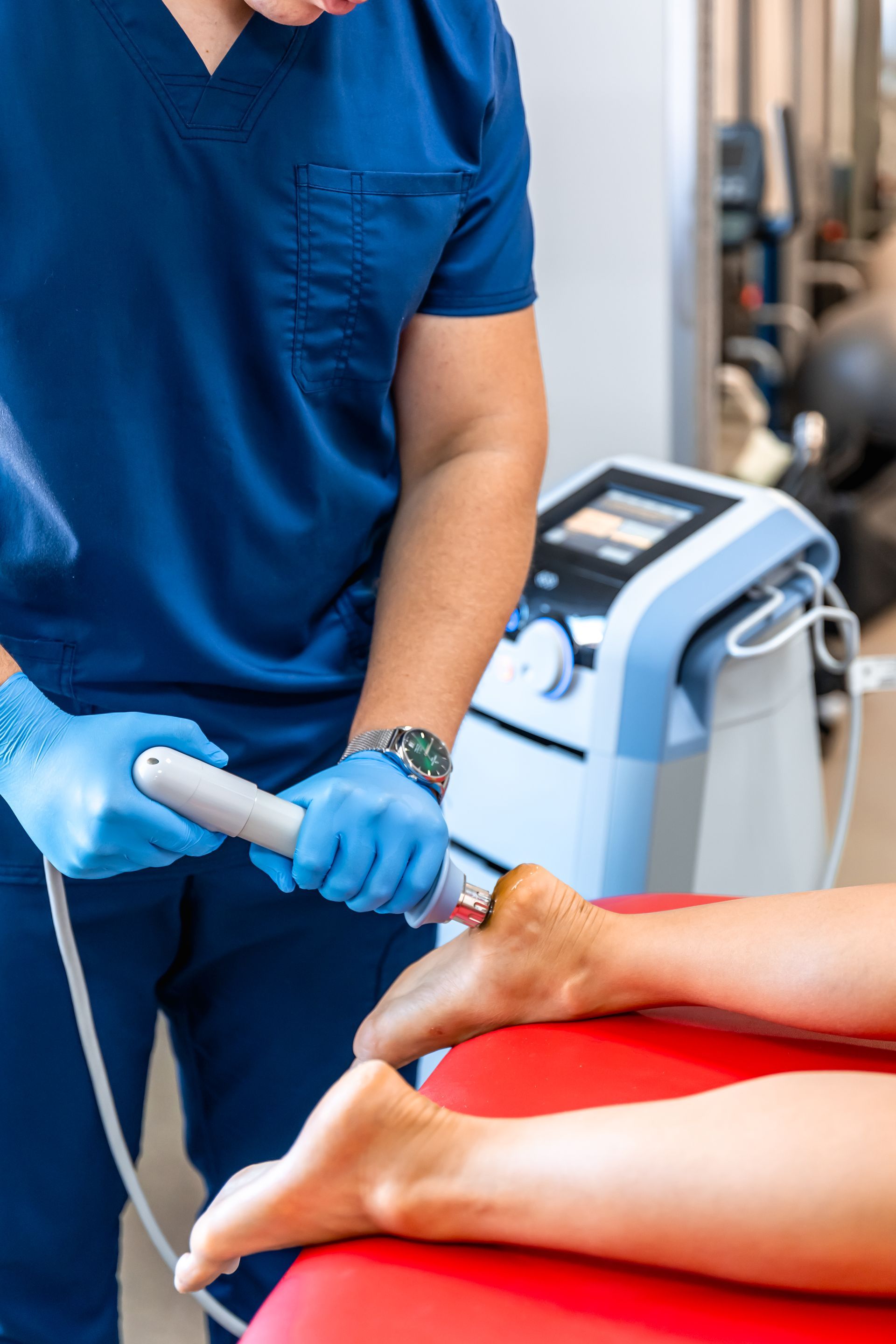
Shock Wave Therapy
Accelerate Healing with ShockWave Therapy
Harness the transformative power of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy at Orthopaedic Sport Institute. This non-invasive treatment utilizes high-frequency sound waves to directly target and alleviate painful areas in your body.
Ideal for individuals dealing with long-standing inflammation, muscle stiffness, or calcification, our therapy promotes accelerated tissue repair, collagen production, and tissue mobility. Witness the significant benefits of new blood vessel formation and trigger point release while we guide you on your path to achieving superior health and enhanced athletic performance.
Rapid Recovery with OUR ShockWave Therapy
Are you grappling with chronic pain or mobility issues due to tendon, ligament, or muscle ailments? Our advanced shockwave therapy service at Orthopaedic Sport Institute is designed for you. Utilizing high-energy sound waves, this therapy accelerates tissue repair, and cell growth, and alleviates pain, ultimately restoring your mobility.
Whether you're an athlete dealing with the aftermath of a vigorous sport or anyone suffering from chronic discomfort, take the first step toward regaining control over your body today with our shockwave therapy.
-
Who is it for
We offer innovative shockwave therapy for individuals struggling with various physical ailments. If you are experiencing chronic discomfort or impaired mobility due to any of the following conditions, our shockwave therapy could be the solution you're seeking:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Heel and arch pain
- Achilles tendon pain
- Calcific tendinosis/tendonitis
- Shin pain/tibial stress syndrome
- Patellar tendonitis
- Chronic neck, shoulder and back pain
- Muscle tension (trigger points)
- Tennis elbow
- Issues with wound healing
-
Our goal
Shockwave therapy aims to accelerate the healing process and alleviate pain. By stimulating tissue repair and cell growth, this innovative treatment restores mobility and function. It's an effective solution for a range of conditions, designed to get you back on your feet faster and living life without limitations.
Benefits of ShockWave Therapy
Discover the transformative power of shockwave therapy at Orthopaedic Sport Institute. Utilizing advanced technology, our expert team delivers effective treatments designed to accelerate recovery and alleviate pain.
-
Quick Pain Relief
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that can provide immediate relief from chronic pain, enhancing your quality of life and restoring your physical strength.
-
Increased Mobility
Shockwave therapy works wonders in improving joint mobility and function. Regular sessions can help restore flexibility and motion range, making daily activities more comfortable.
-
Broad Applications
From treating sports injuries to alleviating chronic ailments such as plantar fasciitis and tennis elbow, shockwave therapy benefits by serving a wide range of applications, ensuring comprehensive care for varied health concerns.
-
Accelerated Healing
The therapy stimulates your body's natural healing process, promoting faster recovery from injuries. It’s an ideal solution for athletes and active individuals seeking to expedite their rehabilitation.
-
Reduced Dependency on Medication
By addressing the root cause of pain, shockwave therapy can minimize reliance on pain medication, offering a natural and sustainable way to manage discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
In our commitment to helping you make informed health choices, we've compiled a list of some frequently asked questions about our shockwave therapy services. Please read on to understand more about this innovative treatment method.
-
Is shockwave therapy safe?
Yes, shockwave therapy is considered to be a safe treatment when administered by trained healthcare professionals like those at the Orthopaedic Sport Institute. It's a non-invasive procedure that doesn't require any anesthesia or medications. As with any medical treatment, your provider will discuss any potential risks with you prior to beginning therapy.
-
What should I expect after a Shockwave Therapy session?
After a session, you may experience minor shockwave therapy side effects like temporary redness, swelling, or slight discomfort in the treated area. These symptoms are typically mild and should resolve within a few days. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities immediately after treatment. It's important to follow any specific post-treatment care instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure optimal healing.
-
Can Shockwave Therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, often shockwave therapy is used in conjunction with other treatments like physiotherapy, chiropractic care or massage therapy to enhance recovery. The combination of treatments can provide comprehensive care and promote faster healing. Your healthcare provider at Orthopaedic Sport Institute will develop a personalized treatment plan based on your specific condition and needs.
other Services
At Orthopaedic Sport Institute, we offer diverse services for optimal health and recovery. Specializing in chiropractic care, physiotherapy, concussion management, and shock wave therapy, our expert team is dedicated to restoring your strength, mobility, and confidence.
-
Chiropractic Care
Photo By: John DoeButton -
Physiotherapy
Photo By: John DoeButton -
Custom Orthotics
Photo By: John DoeButton -
Professional Brace Fitting
Photo by: John DoeButton -
Personal & Group Training
Button -
Massage Therapy
Button -
Laser Therapy
Button -
Orthopaedic Surgery
Button -
Medical Acupuncture
Button -
Concussion Management
Button -
Sports Rehabilitation
Button
Embrace Healing with ShockWave Therapy
Say goodbye to persistent pain with our shockwave therapy at Orthopaedic Sport Institute. Let our professional and dedicated team guide you on your path to recovery. Contact us today and unlock the potential of this innovative treatment to enhance your quality of life.
Orthopaedic Sport Institute
Address
Phone
Business Hours
- Mon, Wed
- -
- Tue, Thu
- -
- Friday
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed